Background.
Vodafone is a British telecommunications services provider. It’s part of the Vodafone Group, one of the largest telecommunications companies in the world, and the third-largest mobile network operator in the United Kingdom. The brand is thus well known and trusted, making its use in this phishing attack even more dangerous.
Here, we’ll be presenting a recent phishing attack campaign that was intercepted by Perception Point’s advanced email security service, in which attackers use advanced techniques to deceive users, including a fake Vodafone login page that could trick even experts.
Step 1: The Phishing Attack Email is Sent to the User
The attack starts with the user receiving an email that contains a URL that leads to a fake website – a Vodafone web hosting site. The website “enrolls” the user in a series of steps, starting with requesting their email address.
The URL
We can see that the attackers spoofed the Vodafone domain (Vodafone.co.uk) and changed it to be very close to the original – in this case, they used Vodafone.co.uk-billingupdate.com – so it looks very similar to a legitimate account update.
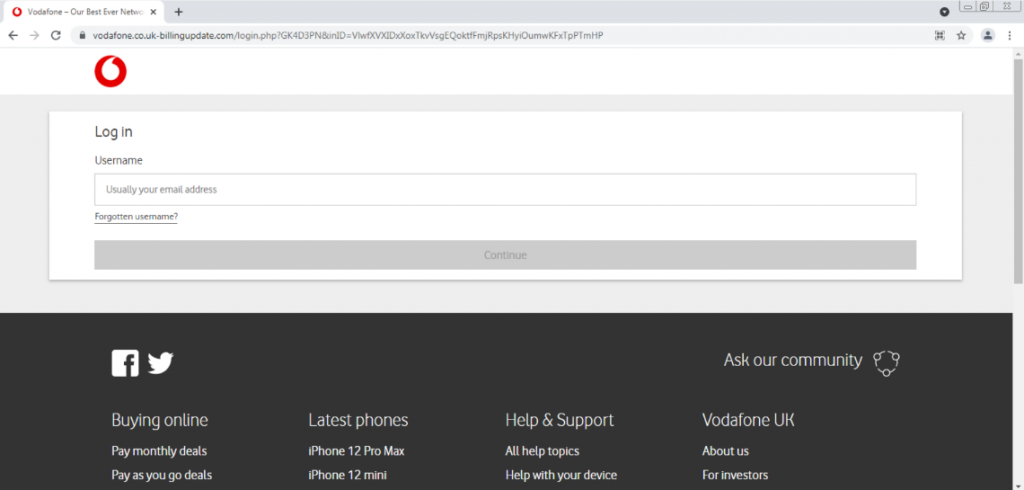
The Website Footer Used in the Phishing Attack
Checking the links in the website footer, in this phishing attack, we observe that they all redirect to the real Vodafone site. This serves to heighten the legitimacy of the website in the eyes of the users.
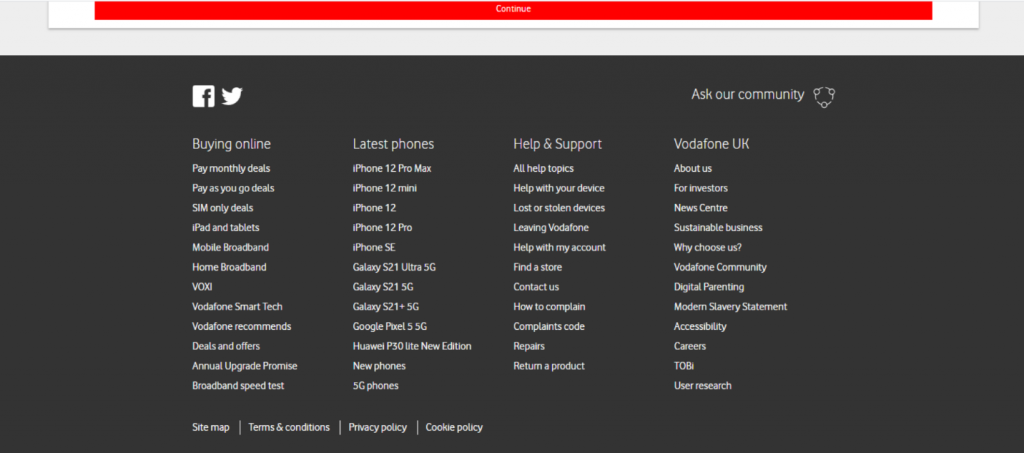
Common Links Used in the Phishing Attack
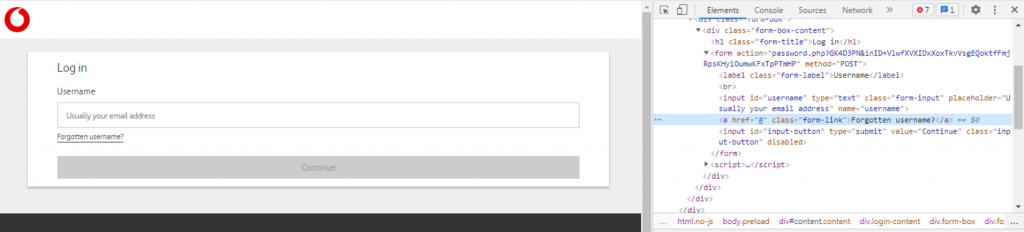
The attackers are smart. In this phishing attack, they include such common links as “Forgotten username,” however these don’t actually work or lead to any page.
After checking the html tags, we can see the “href = #”, meaning these links don’t actually point anywhere.
The Favicon
The attackers also took care of the smaller details. For example, in this phishing attack, they added a favicon in the website tab. A favicon is a small icon used on web browsers to represent a website or a web page. Favicons are most commonly displayed on tabs at the top of a web browser.
Vodafone’s favicon appears in order to increase the authenticity of the login page.
The Website Certificate is Important to Check to Determine a Phishing Attack
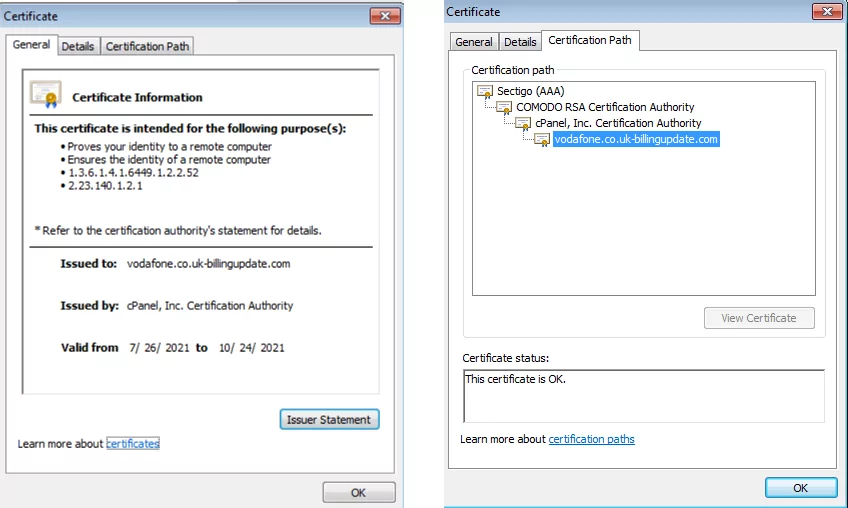
While investigating the website’s certificate, we found that the certificate is new – it was issued on July 26, 2021.
The certificate was issued by the cPanel, Inc. Certification Authority, showing that the website is hosted on cPanel.
cPanel is a hosting site for web apps, and this Vodafone phishing campaign was clearly built using this platform.
Attackers often host phishing websites on sites that can issue certificates, ensuring that they appear as a legitimate website. cPanel is such a website platform.
Step 2: How the Phishing Attack Works
After examining the evidence around this phishing website, we continued with the login procedures in order to learn more about the attack, including what the attackers aim to achieve.
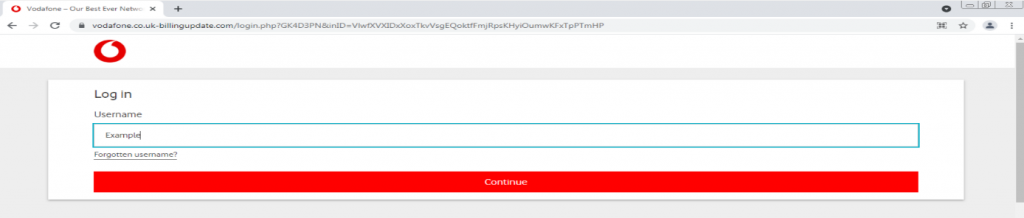
We were able to proceed with a fake user name – in this case, “example.”
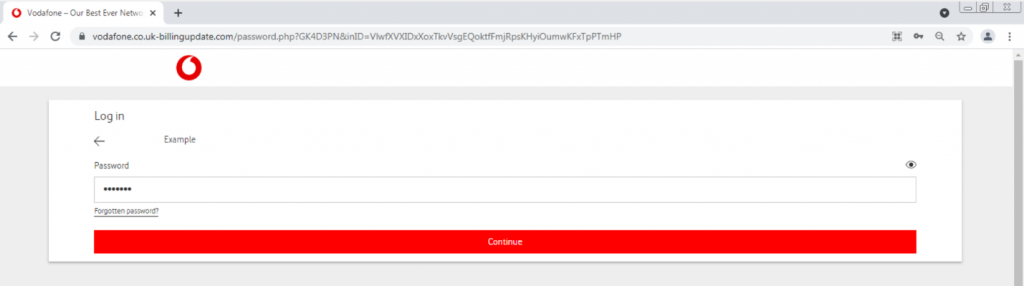
Next, we were asked to enter a password. We entered “1234567.”
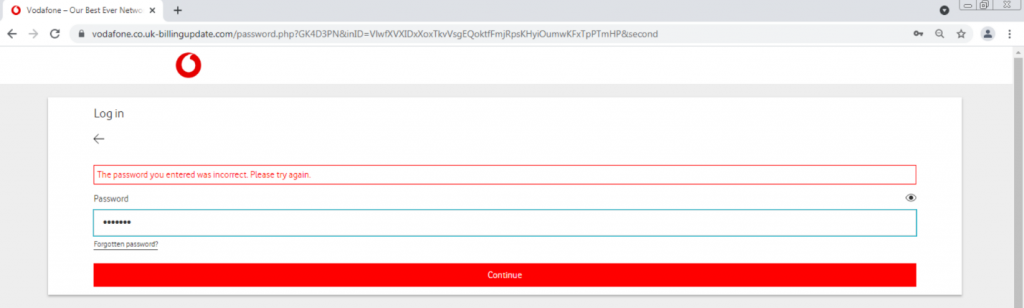
Suddenly, an error appears. This can be seen in the image marked in red. The attacker will likely try to log in with the credentials we inserted on the real Vodafone website; or will just keep the credentials in a database, and try to log in afterwards.
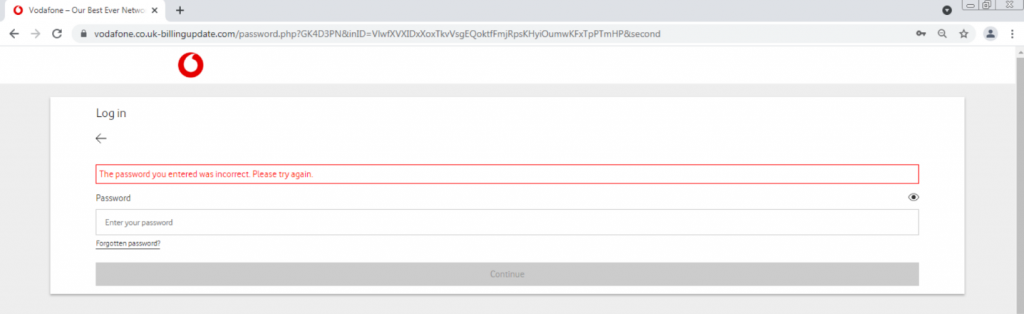
We then entered the same password “1234567”
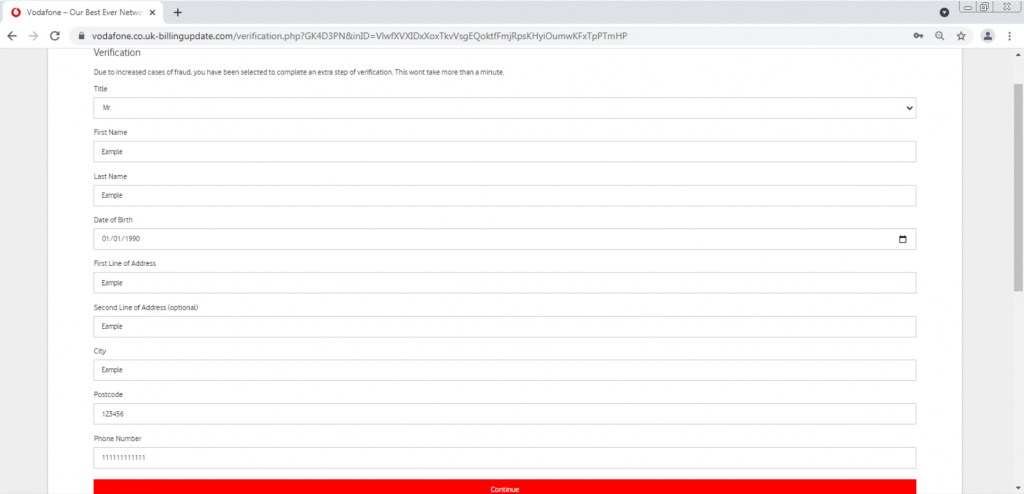
After the user enters their password again, they automatically get redirected to a verification page, with a link that starts with “https://vodafone.co.uk-billingupdate.com” and is meant to trick the user into thinking that it’s part of the vodafone domain.
The user is asked to enter more information, including filling out a form. Ironically, a message appears noting “Due to increased cases of fraud, you have been selected for an extra step of verification, this won’t take more than a minute.”
The attacker is trying to make the website look and feel like a secure website, but in reality is trying to harvest more information from users that can be used in impersonating the user within other websites.
Related content: Read our article about types of phishing attacks.
Step 3: Stealing the Credentials in this Phishing Attack
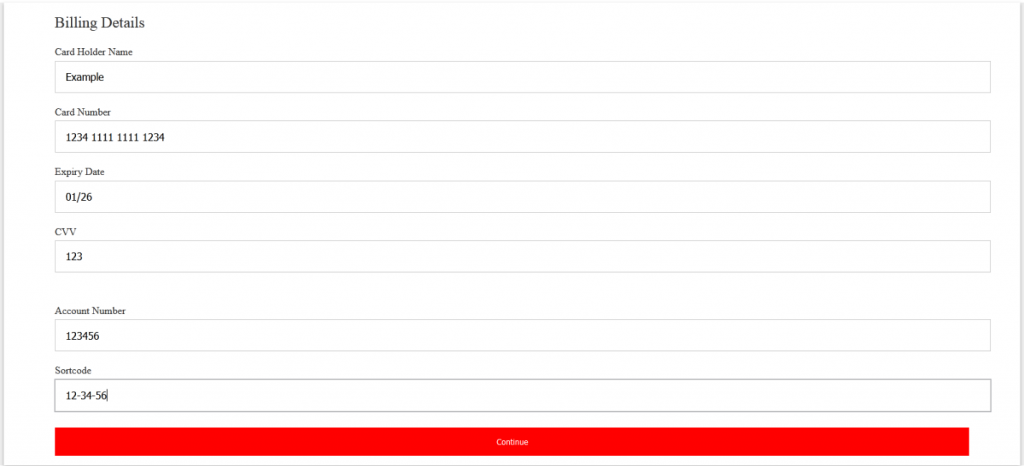
After clicking on “Continue,” the user is redirected to a page that requires the entering of “Billing Details.”
The objective here is very simple: after the user goes through all those initial stages, they fill out simple credit card details.

For example:
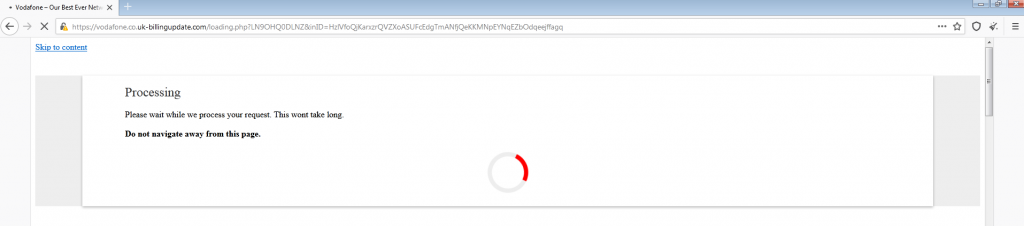
We then clicked on the “continue” button and were redirected to this page, with the words “Processing.”
After a few seconds, we were redirected to another page confirming that the process was completed and our identity was confirmed – and typical in these types of spoofing attempts, we were ultimately redirected to the real Vodafone website.


Related content: Read our guide to phishing detection
Phishing Attack Recommendations.
As we’ve shown, attackers use URLs that are very similar to real domains and pay attention to the little details such as favicons and website security certificates. All of this means that users have to be super vigilant – a difficult task given today’s hectic schedules. So remember:
- When it comes to email security, always check the display name and the sender’s email address. Changing the display name is very common, so validate the email address as well, to decrease the chance of a successful spoofing attempt.
- Attackers are often less concerned about being grammatically correct. Which means that typos and spelling errors are often evident in messages. Such errors in an email could be a good indication that the message is not genuine.
- Question the need for submitting your credit card details – in this case, there is no reason for Vodafone to require the user’s credit card details.
- Avoid clicking links if you are not sure about them. Even better, hover over URLs: if the alternate text does not match the display text, or if it seems strange, DO NOT click on it. If you already clicked a link from an email, inspect the website even if it seems to display non-malicious content.
- Before giving away details, always check if the domain is known to you and that the website is protected by SSL (HTTPS and not HTTP). Also, check the certificate of the website to see who it was issued by, as well as the date it was issued (in our case it was very recent).
- Not sure of the reliability of the website? Try clicking different buttons and see where they lead you. In this case, all of the other buttons on the main page simply didn’t work – not typical behavior, of course.
- To avoid such cases, we recommend actively logging in to the official website, and to check if your account has any outstanding payments.
- You can always try to enter fake details to check the website’s behavior, such as validations on invalid content, and so on.
- Don’t believe everything you see; phishers are extremely good at what they do. Many malicious emails include convincing brand logos, language, and a seemingly valid email address. Be skeptical when it comes to your email messages—if it looks even remotely suspicious, do not open it.
- Use an advanced email security solution that scans 100% of files and URLs, and prevents malicious emails from entering your employees’ inboxes, to ensure your organization is not exposed to vulnerabilities.
Read more about advanced Email security detection technologies to help secure your business.
Download the latest Gartner Email Security Market Guide.