What is Hyper-V?
Hyper-V is a bare-metal (type 1) hypervisor, created by Microsoft in 2016. It is built into most versions of Windows.
Hyper-V can be used to virtualize hardware components and operating systems. It enables running guest operating systems on servers and regular Windows workstations. Hyper-V is commonly used to run Windows VDI workloads. It is also the hypervisor that powers Azure VMs.
There are three consumer versions of Hyper-V:
- Hyper-V Server, a standalone virtualization solution
- Hyper-V for Windows Server
- Hyper-V for Windows 10
In this article
What is VMware ESXi?
VMware pioneered virtualization technology in the 1990s. Its virtualization solutions are based on the ESX/ESXi bare metal hypervisor, for x86 architecture. The hypervisor can be used to run multiple virtual machines (VMs), sharing resources from the same physical server, such as CPU, network interfaces and RAM.
VMware products enable virtualization, software-defined data centers, and management of cloud infrastructure. VMware vSphere is its main server virtualization platform, which enables deployment and management of VMs at large scale.
Related content: read our guide to Hyper-V on Windows 10

Tal ZamirCTO, Perception Point
Tal Zamir is a 20-year software industry leader with a track record of solving urgent business challenges by reimagining how technology works.
TIPS FROM THE EXPERTS
- Utilize nested virtualization for testing environments
Hyper-V supports nested virtualization, allowing you to run a hypervisor inside a virtual machine. This feature is particularly useful for testing complex setups, such as multi-tier applications or training environments, without needing additional physical hardware. - Use Hyper-V Replica for disaster recovery
Hyper-V Replica allows you to replicate a VM from one Hyper-V host to another for disaster recovery purposes. It supports asynchronous replication and can be set to replicate at intervals as frequent as every 30 seconds, which is essential for minimizing data loss in critical environments. - Use Hyper-V Containers for lightweight virtualization
Hyper-V Containers provide a way to run Windows containers with enhanced isolation by running them in a lightweight VM. This is particularly useful when containerized applications require stronger isolation than what is provided by standard containers. - Enhance security with Just Enough Administration (JEA)
Implement JEA in your Hyper-V environment to enforce the principle of least privilege. This allows you to provide users with just enough permissions to perform their tasks without exposing the full management capabilities of Hyper-V, thereby reducing security risks.
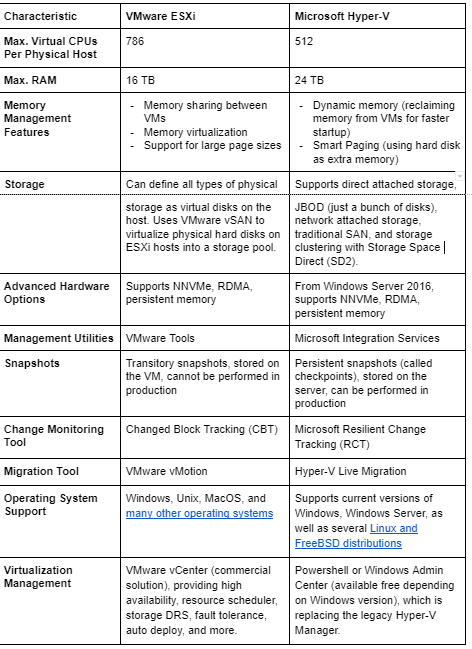
VMware vs Hyper-V: Technical Characteristics
When comparing VMware and Hyper-V, we’ll focus on ESXi, the hypervisor powering VMware’s virtualization stack. The following table compares the key technical characteristics of ESXi as compared to Hyper-V.
VMware Pricing vs Hyper-V Pricing
Both ESXi and Hyper-V are free to download, and can be used for free without limitation on the CPUs, RAM or storage on the host. But while the hypervisor itself is free, the management layer is provided at extra charge.
The prices below are correct as of the time of this writing—please consult vendor websites for up to date pricing.
VMware pricing for virtualization management
VMware vSphere is the basic virtualization management product used with ESXi. The entry level editions are:
- VMware vSphere Essentials—supports 3 servers with 2 processors each, priced at $510 per year
- VMware vSphere Essentials Plus—same as Essentials, with additional features, priced at $5,596 per year
- VMware vSphere Standard—requires vCenter, priced at $1,268 per physical processor per year
Hyper-V pricing for virtualization management
Microsoft recommends that users upgrade to Windows Server and pay for Windows System Center for virtualization management. However, basic features like creating a VM, snapshots and resource allocation are free.
- Windows System Center license costs start from $1,323 per year
- Windows Server 2019 license costs are $501 per year for the Essentials edition, $972 for the Standard edition and $6,155 for the Datacenter edition with full virtualization features
VMware NSX vs Microsoft Hyper-V Networking
VMware provides NSX-T for virtualized networking, which supports the following features:
- Layer 2, Layer 3, and isolated virtual networks
- L2VPNs enable extending on-premises subnets to the virtualized environment without changing IP addresses
- IPsec VPNs, either route-based with BGP, or policy based, make it possible to connect on-premises networks and VPCs
- Support for AWS Direct Connect (DX) for high speed connectivity between on-premise data centers and AWS
- Native DHCP capabilities, with the ability to connect to on-premises IPAM devices
- Create multiple DNS zones, allowing use of different DNS servers for network subdomains.
- Take advantage of distributed routing, managed by an NSX kernel module running on the host where the workload resides, so workloads can efficiently communicate with each other.
Microsoft Hyper-V provides networking via Windows Server. Windows Server virtualized networking features include:
- Virtualized Layer 2 networks
- Traffic routed between virtual networks or between physical and virtual networks via gateways
- Virtual Extensible LAN (VLAN) and Generic Routing Encapsulation (NVGRE)
- Software defined networking (SDN)
VMware Security vs Hyper-V Security
VMware is an enterprise-grade virtualization solution, and naturally, its security features are more robust. However, Hyper-V also provides robust security features.
The ESXi hypervisor is protected by the following security features:
- Host-level security capabilities—ESXi supports CPU isolation, memory isolation, device isolation, lockdown mode, certificate replacement, and smart card authentication.
- Host firewall—ESXi hosts are protected by a firewall, which denies access to services and ports by default, except for a limited number of essential ports.
- Host Certificates—the VMware certificate infrastructure grants each ESXi host a certificate signed by the VMware Certificate Authority (VMCA).
- Secure defaults—VMware places controls on several configuration parameters that can enable intrusion or misuse. Users can change these parameters, at their own risk, ensuring they are operating in a secured environment.
- Strong encryption—all communication between ESXi and clients is secured using SSL, by default, with the strong SHA-256 RSA algorithm.
- UEFI Secure Boot—you can run VMs in secure boot mode to prevent them from loading any application that is not verified via certificate.
Hyper-V security features include:
- Encrypted networks—new in Windows Server 2019, performs encryption for all traffic on an entire subnet. Does not require any configuration or changes to virtual machines or network equipment.
- Guarded Fabric – a security model that protects hosts and their VMs from malicious software. Guarded fabrics can run three normal VMs with no protection, encryption-supported VMs, and shielded VMs with protection that cannot be disabled.
- Host Guardian Service (HGS) – a component in the Guarded Fabric framework, ensures that Hyper0V hosts are known to the organization, healthy, and running trusted software. It does this using an Attestation Service and a Key Protection Service (KPS).
- Shielded VMs – generation 2 VMs that have a virtual trusted platform module (vTPM), are encrypted with BitLocker, and can only be run on hosts attested and approved by HGS.

Hyper-V is a bare-metal (type 1) hypervisor, created by Microsoft in 2016. It is built into most versions of Windows.
VMware pioneered virtualization technology in the 1990s. Its virtualization solutions are based on the ESX/ESXi bare metal hypervisor, for x86 architecture. The hypervisor can be used to run multiple virtual machines (VMs), sharing resources from the same physical server, such as CPU, network interfaces and RAM.