Overview
Zoom (NASDAQ:ZM) is one of the most prominent tech companies in the world today. In early December, the company was being traded at a staggering $110 billion dollars. It recently reported its quarterly revenue of $777 million in November 2020. This represents a 367% increase year-over-year.
This tremendous growth is due to many factors. However, there’s no doubt that the COVID-19 pandemic is the main one. As more countries enforce lockdowns, more enterprises are adjusting their methods of working. For many, this includes working remotely.
Zoom came out on top as one of the best solutions the remote-working world. It gives users the ability to hold meetings and arrange digital events via Zoom Webinar.
The Driver behind Phishing.
By looking at the numbers below, it’s easy to see the prevalence of Zoom across enterprises and end-users. In 6 months’ time, the peak daily participants of Zoom soared from 10 million to 300 million, which is a 30x growth.
But, unfortunately, there’s no good without bad. That’s life. And as more people use a new app, threat actors will use it for their malicious purpose. Attackers know that like any application, Zoom also requires an identification to sign in to the app. And once a log-in page is necessary, a new loophole for stealing credentials pops into the attackers’ eyes.
The Correlation.
Perception Point constantly monitors phishing trends. One of the most important identifications any security expert should notice is what the most used brands for phishing are.
Our IR team found that Zoom has been one of the most “phished” brands this year. The company also has the highest growth of unique phishing attempts. Over the last 6 months, the number of phishing attacks leveraging Zoom raised by 167%(!). This means, that on average, the number of Zoom-based phishing rose by 17.8% month-over-month.
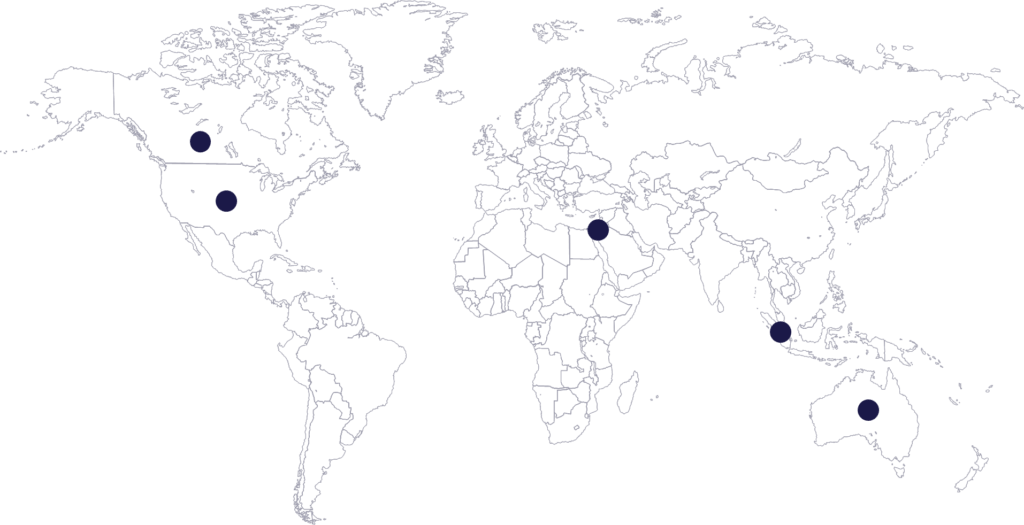
In terms of global reach, we can see that attackers are targeting companies across the globe. Overall, 100% of our customer and prospect based were the target of a Zoom-based attacks.
In the map below, we marked the top-5 most attacked countries based on data from our system.
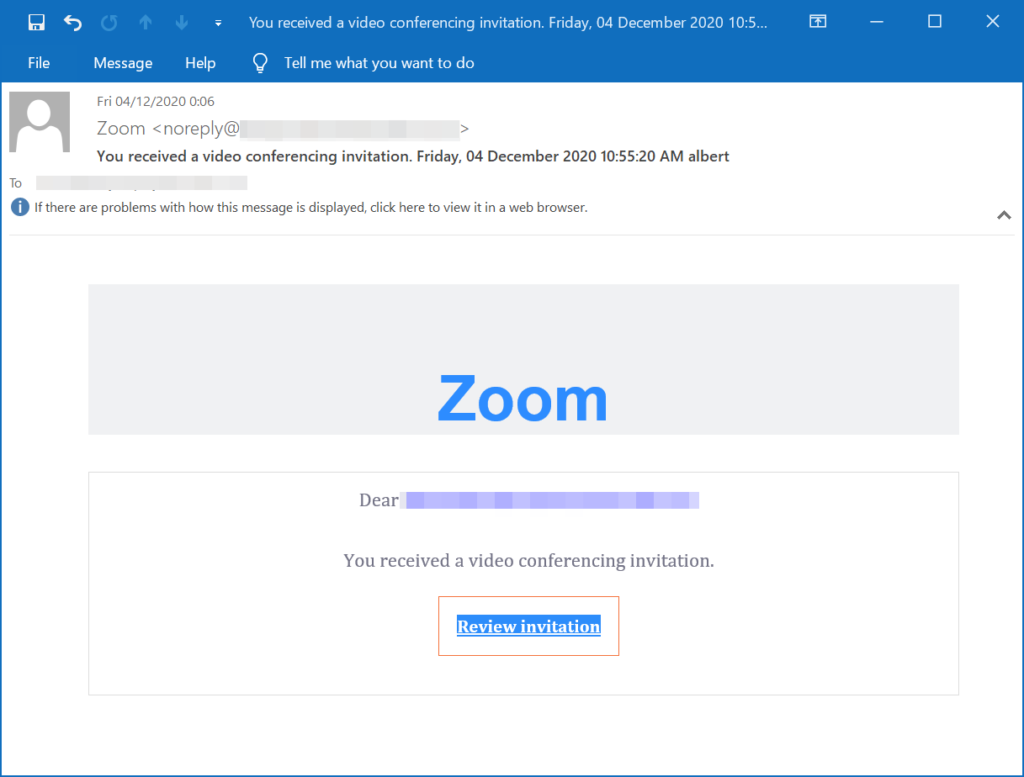
Examples.
The vast majority of Zoom phishing attacks are using the same techniques:
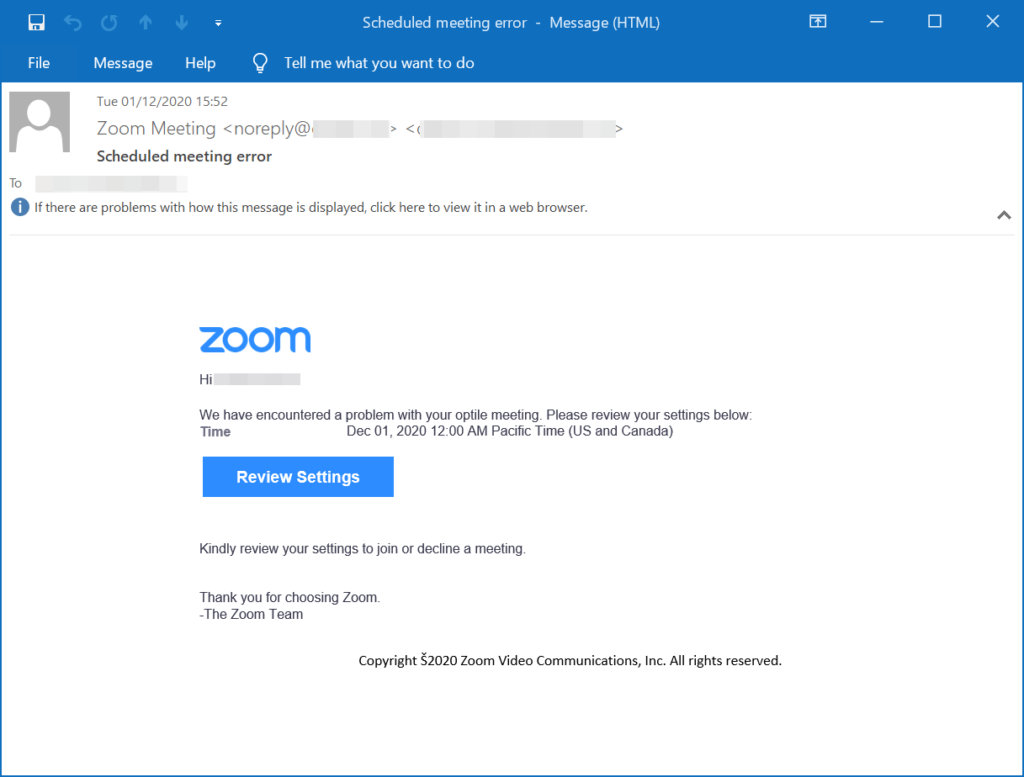
- Brand assets. This includes highlighting the Zoom logo, using the brand color, and adding fake signatures.
- Spoofing. This includes both domain spoofing and display-name spoofing.
- Malicious link. The email itself includes a link to a “meeting.” The link is actually a fake login page that ends up stealing credentials.
Perception Point.
- Image-recognition engine. This uses advanced image-recognition algorithms to confirm the URL is a legitimate site. This is a fully dynamic engine that also scans all attempts to phish the assets of the targeted company.
- Recursive Unpacker. This is an anti-evasion engine that unpacks all embedded phishing attacks, no matter how they’re concealed by the attacker.
- URL reputation. This uses data from the top four URL reputation engines monitoring global traffic for phishing attempts.
- Threat intelligence. This leverages intelligence from external security vendors and the cyber community.
We welcome you to check our anti-phishing capabilities, and see how we can prevent the next attack on your organization. If you want to install the Perception Point solution in your organization, you can also simply contact us. We will make sure to do the heavy lifting.