The Perception Point Incidence Response Team recently reported on a new CEO Fraud phishing kit that leverages Backblaze, a cloud-storage tool, to host fake Office 365 login pages. (BackBlaze users can report attacks here.)
Phishing and BEC have grown so big that there’s an entire criminal market around it. Phishing-as-a-Service is when hackers buy pre-existing phishing software. This makes it easier than ever to rapidly launch an attack without any prior coding knowledge.
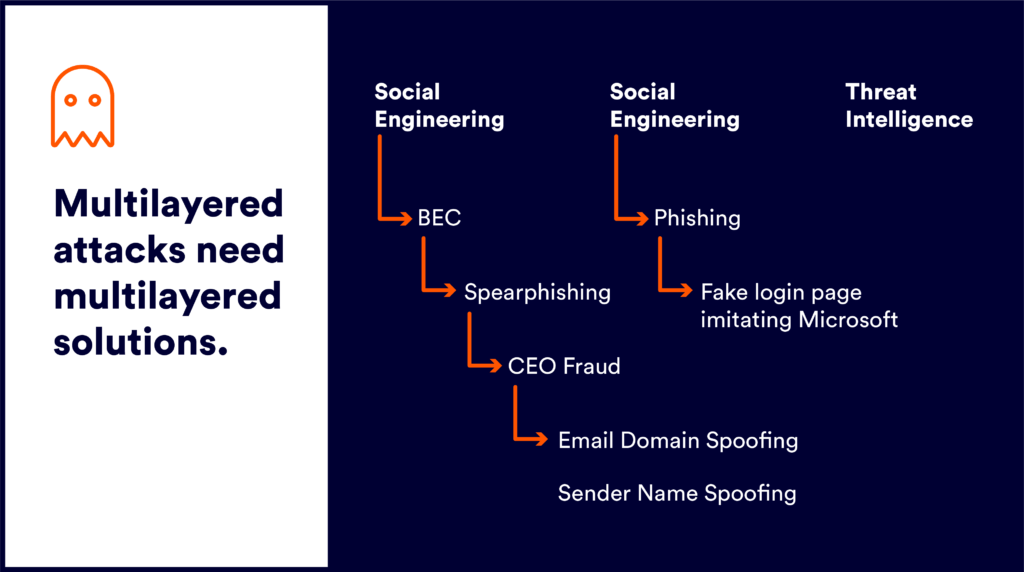
Three Methods of CEO Fraud
Before we dive into the aforementioned phishing kit, let’s first discuss the methods used by perpetrators of CEO Fraud.
- Account Takeover. An attacker takes over a real email address, either by brute-force tactics or some form of social engineering that allowed them the password of the email address.
- Email Address Domain Spoofing. A common form of phishing that occurs when an attacker uses a company’s domain in email communication to impersonate one of its employees.
- Sender Display Name Spoofing. This is when the display name looks like it’s from a real person in the company. The attacker is hoping that the receiver of the email will not see the actual email address that it is coming from. For mobile users, for example, they only see the display name and not the actual email address.
In the following example, you can see how one attacker attempted to phish private company information from Company “A.” To do this, he or she posed as the CEO of Company B, a well-known partner of Company A.
The Malicious Methodology Used in the CEO Fraud Phishing Attack
Step 1. CEO Fraud – Spoofing the CEO
- The attacker sends an email to employees at Company A, telling them to download an important document. He or she poses as authentic by perfectly spoofing the sender name and domain to match the real CEO’s details.
- Spoofed Sender Display Name (the name that appears next to the email address).
- Spoofed Sender Company Domain (the part that comes after the ‘@’ symbol).
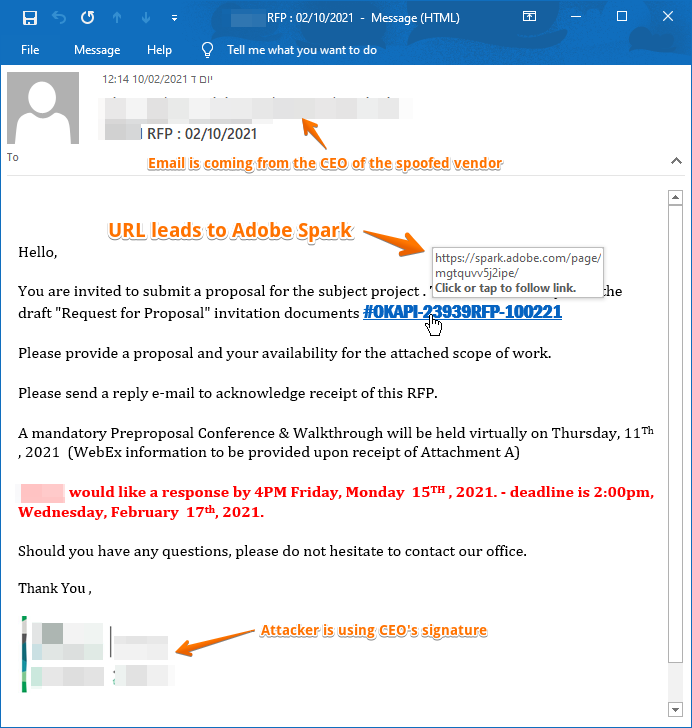
Step 2. CEO Fraud – Creating Legitimacy
- The attacker creates a phishing page and hosts it on Adobe. The employee is then sent to a page hosted on Adobe Spark to download the malicious document.
- Phishing Link
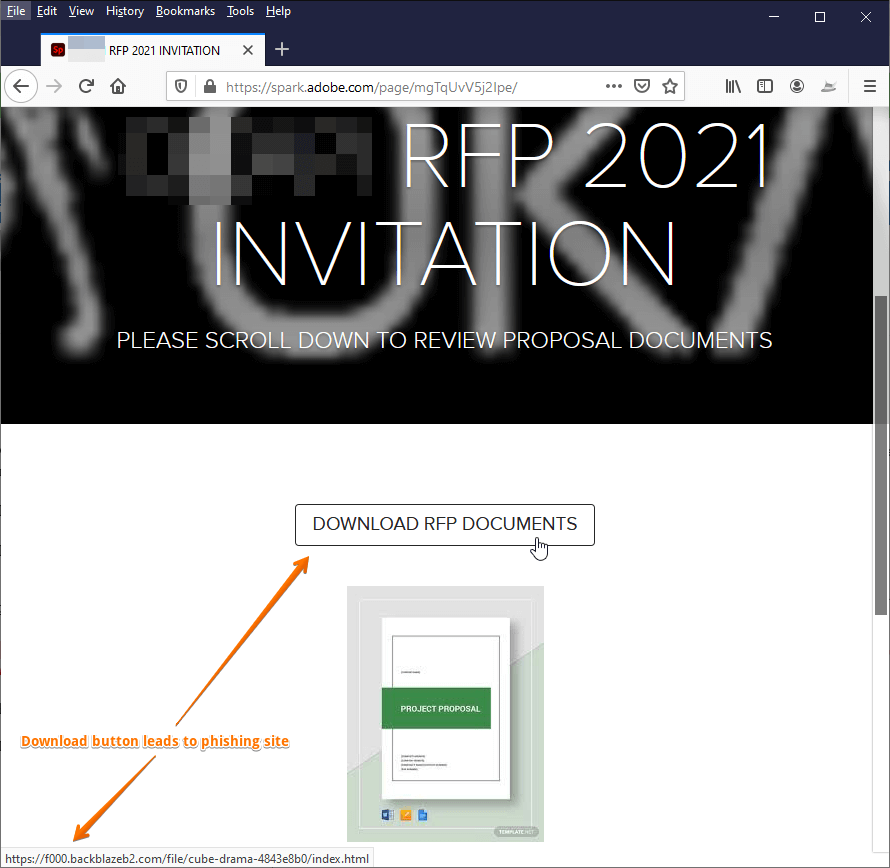
By hosting the page on the well-loved brand Adobe Spark, the attacker is hoping to legitimize the campaign.
Step 3. CEO Fraud – Designing the Phishing Login Page
- The phishing link takes the user to the fake login page designed to look like a real Microsoft page. The attacker created the phishing page using Backblaze, a cloud storage platform that allows users to publish a page using the Backblaze domain as its host.
- Phishing Login Page
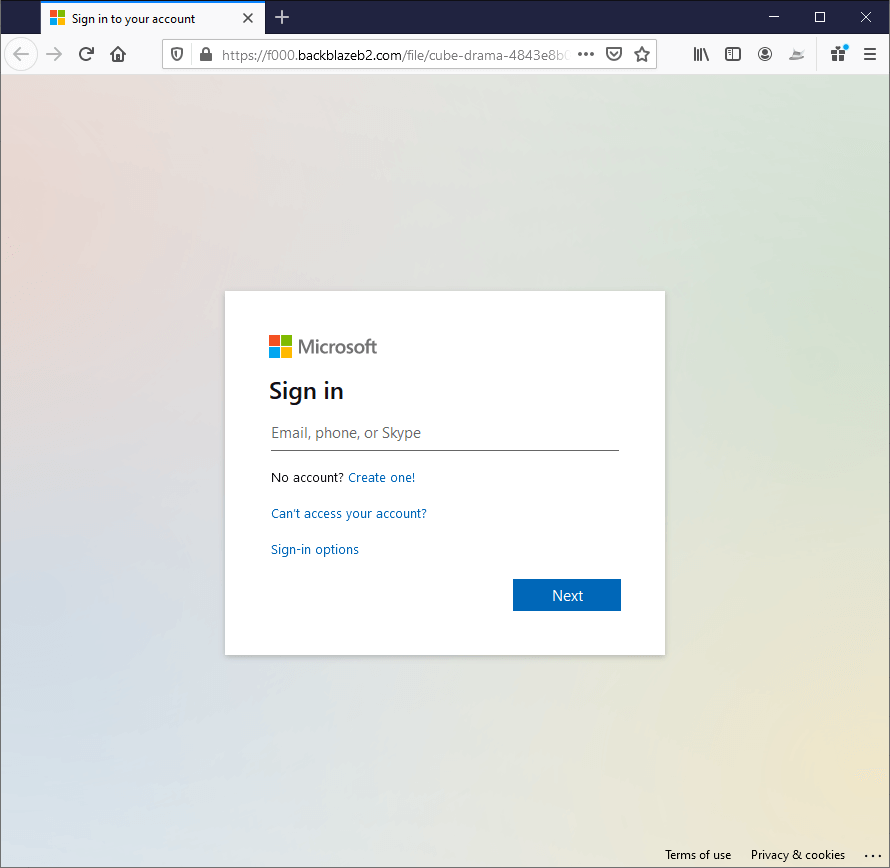
Step 4: CEO Fraud – Obtaining the Credentials
As soon as the victim fills in the form, it’s game over, unfortunately. The details have been successfully phished.

How to Protect Your Organization
To combat impersonation attacks (both Email Address Spoofing and Display Name Spoofing), it’s important that every incoming email in the organization is pre-screened using anti-phishing services.
It Might Look the Same to You But Not to Our Algorithms.
Perception Point developed unique algorithms to prevent all types of impersonation techniques.
Machine-learning tech inspects all relevant data and metadata to identify any deviation from standard operations and to detect suspicious content well ahead it reaches the end-user who might be tricked.
Learn more about our unique algorithms for fighting all types of BEC.